We demonstrated that choline is an endogenous agonist of Sigma-1 receptors, intracellular receptors located on the endoplasmic reticulum. Choline, released subsequent to GPCR stimulation by various agonists, activates Sigma-1 receptors and potentiates IP3-evoked Ca2+ signals.
Brailoiu Research
1025 Walnut Street
College Building, Room 301
Philadelphia, PA 19107
- 215-503-6866
- 215-503-7468 (Office)
Highlighted Publications
Brailoiu E, Chakraborty S, Brailoiu GC, Zhao P, Barr JL, Ilies MA, Unterwald EM, Abood ME, Taylor CW. Choline Is an Intracellular Messenger Linking Extracellular Stimuli to IP(3)-Evoked Ca(2+) Signals through Sigma-1 Receptors. Cell Rep. 2019 Jan 8;26(2):330-337.e4. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6326163.
Brailoiu E, Barr JL, Wittorf HN, Inan S, Unterwald EM, Brailoiu GC. Modulation of the Blood-Brain Barrier by Sigma-1R Activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10) PubMed Central PMCID: PMC11121402.
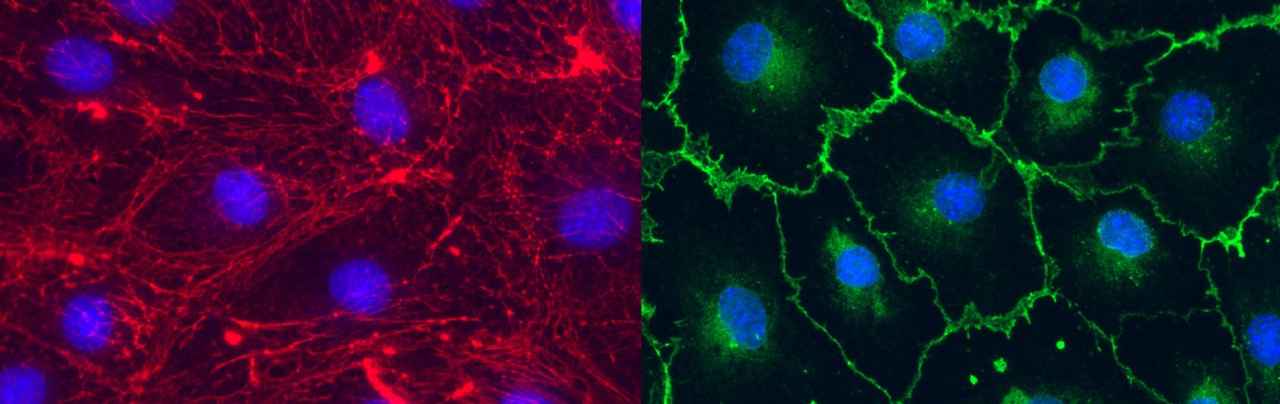
In this study, we investigated the effect of Sigma-1R activation in vitro on rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (RBMVEC), an important component of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), and in vivo on the BBB permeability in rats. Sigma-1R activation promoted oxidative stress and disruption of tight and adherens junctions, and increased the BBB permeability visualized in vivo in awake rats with a miniature integrated fluorescence microscope (aka, miniscope; Doric Lenses Inc.).
Barr JL, Lindenau KL, Brailoiu E, Brailoiu GC. Direct evidence of bradycardic effect of omega-3 fatty acids acting on nucleus ambiguus. Neurosci Lett. 2020 Sep 14;735:135196. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7484120.
Neurons of nucleus ambiguus provide the parasympathetic control of heart rate. Using in vitro (calcium and voltage imaging) and in vivo (heart rate measurement) approaches, we found that docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, decreases heart rate in rats by activation of FFA1 receptor on cardiac-projecting nucleus ambiguus neurons.
Publications
- Choline—An Essential Nutrient with Health Benefits and a Signaling Molecule
- Modulation of the Blood–Brain Barrier by Sigma-1R Activation
- Two-pore channel-2 and inositol trisphosphate receptors coordinate Ca2+ signals between lysosomes and the endoplasmic reticulum
- Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Mediated by FFA1 Receptor—Evidence Using Miniscope
- Choline-sigma-1r as an additional mechanism for potentiation of orexin by cocaine
- Assessment of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Using Miniaturized Fluorescence Microscopy in Freely Moving Rats
- Direct evidence of bradycardic effect of omega-3 fatty acids acting on nucleus ambiguus
- 1-chromonyl-5-imidazolylpentadienone demonstrates anti-cancer action against tnbc and exhibits synergism with paclitaxel
- Acute cocaine administration alters permeability of blood-brain barrier in freely-moving rats— Evidence using miniaturized fluorescence microscopy
- GPR55-mediated effects on brain microvascular endothelial cells and the blood–brain barrier
- Choline Is an Intracellular Messenger Linking Extracellular Stimuli to IP 3 -Evoked Ca 2+ Signals through Sigma-1 Receptors
- Effects of Platelet-Activating Factor on Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Modulation of cardiac vagal tone by bradykinin acting on nucleus ambiguus
- HIV Tat excites D1 receptor-like expressing neurons from rat nucleus accumbens
- Mechanisms of modulation of brain microvascular endothelial cells function by thrombin
- Effects of VPAC1 activation in nucleus ambiguus neurons
- Modulation of calcium entry by the endo-lysosomal system
- Fusion of lysosomes with secretory organelles leads to uncontrolled exocytosis in the lysosomal storage disease mucolipidosis type IV
- Cocaine inhibits store-operated Ca2+ entry in brain microvascular endothelial cells: Critical role for sigma-1 receptors
- Mechanisms of activation of nucleus accumbens neurons by cocaine via sigma-1 receptor-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-transient receptor potential canonical channel pathways
